Event Broadcasting
Coravel's event broadcasting allows listeners to subscribe to events that occur in your application.
This is a great way to build maintainable applications who's parts are loosely coupled!
For example, you want to add a feature that sends a twitter tweet and an e-mail updating your social network about any new posts you add to your blog:
Config
In your startup file, in the ConfigureServices method:
services.AddEvents();
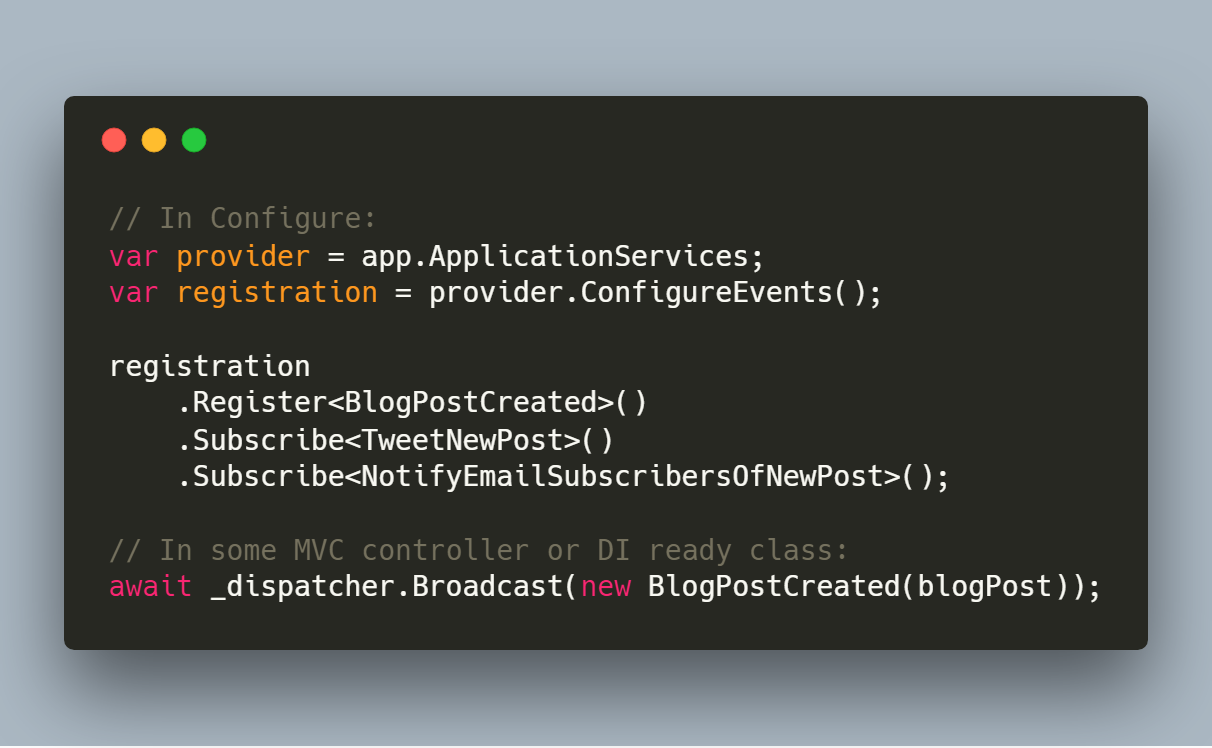
Next, in the Configure method:
var provider = app.ApplicationServices;
IEventRegistration registration = provider.ConfigureEvents();
Now you can start registering events and their listeners:
registration
.Register<BlogPostCreated>()
.Subscribe<TweetNewPost>()
.Subscribe<NotifyEmailSubscribersOfNewPost>();
Creating Events And Listeners
Events
Create a class that implements the interface Coravel.Events.Interfaces.IEvent. That's it!
An event is merely a data object that will be supplied to each listener. It should expose data that is associated with this specific event.
For example, a BlogPostCreated event should accept the BlogPost that was created and then expose it via a public property.
public class BlogPostCreated : IEvent
{
public BlogPost Post { get; set; }
public BlogPostCreated(BlogPost post)
{
this.Post = post;
}
}
Listeners
Create a new class that implements the interface Coravel.Events.Interfaces.IListener<TEvent> where TEvent is the event that you will be listening to.
TIP
Each listener can only be associated with one event.
The IListener<TEvent> interface requires you implement HandleAsync(TEvent broadcasted).
Using the example event in the previous section, we might create a listener named TweetNewPost:
public class TweetNewPost : IListener<BlogPostCreated>
{
private TweetingService _tweeter;
public TweetNewPost(TweetingService tweeter){
this._tweeter = tweeter;
}
public async Task HandleAsync(BlogPostCreated broadcasted)
{
var post = broadcasted.Post;
await this._tweeter.TweetNewPost(post);
}
}
WARNING
Don't forget to register your listener with the service container by using AddTransient or AddScoped.
Using The CLI
You can use Coravel's CLI to generate events and listeners for you.
Broadcasting
Basic
Inject an instance of Coravel.Events.Interfaces.IDispatcher into your controllers or other DI ready classes.
By using the Broadcast method, you may broadcast a new event.
public BlogController : Controller
{
private IDispatcher _dispatcher;
public BlogController(IDispatcher dispatcher)
{
this._dispatcher = dispatcher;
}
public async Task<IActionResult> NewPost(BlogPost newPost)
{
var postCreated = new BlogPostCreated(newPost);
await _dispatcher.Broadcast(postCreated); // All listeners will fire.
}
}
Queuing
If your listeners do some heavy or long-winded work, then you might want to do that in the background (e.g. not on the current HTTP request).
See the docs for queue event broadcasting.